As the holy month of Ramadan continues, millions of Muslims around the world are fasting from dawn to dusk, abstaining from food and devoting their time to worship and good deeds. During this month, people experience changes in the quality of food as well as eating patterns. Many of the traditional home-cooked foods consumed during this time are rich in carbohydrates and proteins. Also, the unusual timing of these meals- one at sunrise (Suhoor) and the next one at sunset (Iftar)-are known to contribute to some major metabolic changes in the body of a fasting person.
It is widely believed that metabolic changes can directly impact your cardiovascular health. Being one of the leading causes of death around the world cardiovascular diseases are studied diligently even today. This in turn has brought to light that metabolic comorbidities such as obesity, insulin resistance and abnormal lipid profile are some of the root causes for the onset of these diseases.
So in this blog, we will examine how Ramadan fasting can reduce the risk of cardiovascular conditions in patients.
Understanding cardiovascular disease
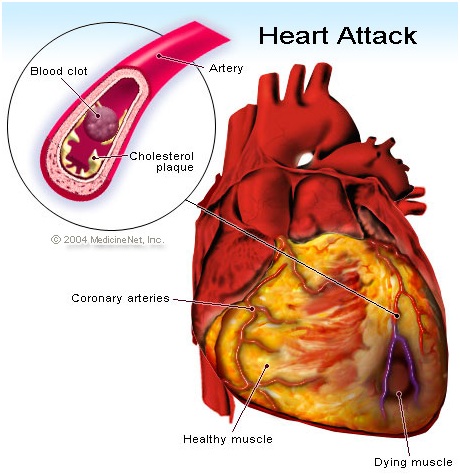
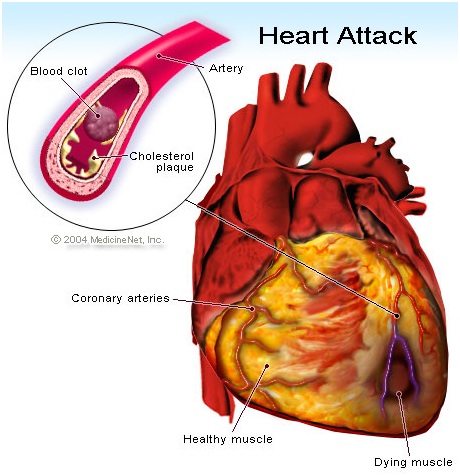
Any disease affecting the heart or the blood vessel comes under cardiovascular diseases. These include coronary artery disease like angina, heart attack and other conditions such as stroke, hypersensitive heart disease, heart failure, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, thromboembolic disease, carditis, peripheral artery disease, aortic aneurysms and venous thrombosis.
According to studies, it is estimated that around 90% of all cardiovascular diseases are preventable. Some of our best cardiologists have noted that improving the risk factors of cardiovascular diseases is the best way to avoid developing any of these conditions. General lifestyle changes like healthy eating habits, exercising, limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco smoking are highly beneficial in improving cardiovascular health. Other risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes and blood lipids should be treated alongside to prevent the onset of cardiovascular disease.
Effects of diet and fasting on cardiovascular diseases
Cardiologists also associate specific foods with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. For instance, high dietary intake of saturated fat, trans-fat and salt along with low intake of vegetables, fruits and fish are linked to increased cardiovascular risk. Reducing the intake of trans-fat helps in keeping blood lipid levels stable.
It is also observed that people who frequently consume high-energy foods such as processed foods high in fats and sugars are more susceptible to obesity, which in turn increase their cardiovascular risk. Sugar intake has always been associated with an increased risk of diabetes mellitus (commonly known as Type 2 diabetes), which in turn adversely affect heart health.
Likewise, increased consumption of dietary salt is known to hinder blood pressure levels, thereby increasing the risk of heart diseases. Dietary salt is found in large quantities in processed meats. Substantial evidence from several cynical trials shows that reducing the consumption of processed meats, specifically red meat can reduce the risk of coronary heart disease.
At the same time, many of the best cardiologists in Dubai see fasting as a beneficial routine that can help reduce the risk of heart disease. Most cardiovascular diseases are linked to excessive weight, cholesterol, hypertension and diabetes. Fasting can help control all four of these factors, thereby improving heart health.
Effects of Ramadan Fasting on heart health
Ramadan is a special time of the year when devoted Muslims take the path of self-reflection, improvement and devotion to worship Allah through selfless actions. Fasting during the holy month is considered one of the five pillars of the Islamic faith, which helps them get closer to God. Apart from the religious significance of fasting, this practice provides a lot of health benefits to the people. During fasting, the cells are put under stress, which forces the body to use fat as its primary source of energy. This helps to reduce weight, as well as maintain blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Ramadan fasting also helps people in resetting their metabolic issues by forcing their bodies to burn calories better during the fasting hours. By balancing out metabolic syndrome, fasting helps a cardiovascular patient reduce his/her risk factors considerably.
Research also shows that there is a significant reduction in weight of Type 2 diabetic patients, which in turn help lower their blood sugar levels. Ramadan fasting has shown a moderate effect on glycaemia and lipoprotein levels of Type 2 diabetic patients which are considered good for them. An independent study in 2012 cited that there is a significant improvement in 10 years of coronary heart disease risk score and other cardiovascular risk factors such as weight, BMI and weight circumference in cardiovascular patients during the month of Ramadan. This further helped cardiologists in concluding that fasting may be useful to improve cardiovascular risk factors.
However, it is to be noted that to reap the benefits of fasting, experts also stress the importance of including fibre-rich fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meat and plant proteins in your diet. A carbohydrate-rich Suhoor will help provide the right amount of calories for the body to function well throughout the day. It will set the metabolism on track by utilizing most of the nutrients from the food consumed, keeping your energy levels up. Along with good food, you should also keep yourself hydrated with water and fresh juices instead of carbonated drinks to balance the electrolyte levels in the body.
You should also take care not to overeat during Suhoor and Iftar. While fasting allows the body to use up excess reserves, overeating can undo its benefits and put a load on your cardiovascular system.
Conclusion
Ramadan fasting has shown to lower the risk score of generally healthy people as well as patients suffering from long term cardiovascular diseases. By improving the metabolism, reducing weight, maintaining a healthy BMI and managing blood sugar levels and blood pressure values, fasting can effectively serve as a wellness program for cardiovascular patients. Fasting has also shown to have a positive impact on brain productivity by creating a state of stress and releasing the “brain-derived neurotrophic factor” – or BDNF – which helps to promote brain stem cell rejuvenation. In short, experts are happy to give their green light for fasting during the holy month.
If you have concerns regarding your cardiovascular health or need a more detailed consultation for the same, visit our cardiology hospital in Dubai today.
Author:

Dr. Kais Mrabet
Specialist Interventional Cardiologist
 Tobacco smokers (cigarettes, waterpipes, bidis, cigars, heated tobacco products) may be more vulnerable to contracting COVID-19, as the act of smoking involves contact of fingers (and possibly contaminated cigarettes) with the lips, which increases the possibility of transmission of viruses from hand to mouth. Smoking waterpipes, also known as shisha or hookah, often involves the sharing of mouth pieces and hoses, which could facilitate the transmission of the COVID-19 virus in communal and social settings.
Tobacco smokers (cigarettes, waterpipes, bidis, cigars, heated tobacco products) may be more vulnerable to contracting COVID-19, as the act of smoking involves contact of fingers (and possibly contaminated cigarettes) with the lips, which increases the possibility of transmission of viruses from hand to mouth. Smoking waterpipes, also known as shisha or hookah, often involves the sharing of mouth pieces and hoses, which could facilitate the transmission of the COVID-19 virus in communal and social settings. Given the risks to health that tobacco use causes, WHO recommends quitting tobacco use. Quitting will help your lungs and heart to work better from the moment you stop. Within 20 minutes of quitting, elevated heart rate and blood pressure drop. After 12 hours, the carbon monoxide level in the bloodstream drops to normal. Within 2-12 weeks, circulation improves and lung function increases. After 1-9 months, coughing and shortness of breath decrease. Quitting will help to protect your loved ones, especially children, from exposure to second-hand smoke.
Given the risks to health that tobacco use causes, WHO recommends quitting tobacco use. Quitting will help your lungs and heart to work better from the moment you stop. Within 20 minutes of quitting, elevated heart rate and blood pressure drop. After 12 hours, the carbon monoxide level in the bloodstream drops to normal. Within 2-12 weeks, circulation improves and lung function increases. After 1-9 months, coughing and shortness of breath decrease. Quitting will help to protect your loved ones, especially children, from exposure to second-hand smoke.