Finding out that you have ovarian cysts during a routine pelvic checkup can be a scary experience for any women. Most women immediately jump to conclusions about their condition and it’s severity. However, not all cysts are dangerous and malignant. For instance, ovarian cysts are one of the most common kinds of cysts that develops on a woman’s ovaries. Many women will develop at least one cyst during their lifetime.
However, cysts can be the cause of one or more menstrual discomforts and their prolonged presence can lead to female infertility. So in this blog, we will discuss more about ovarian cysts, their symptoms and how our gynecologists will treat the condition once diagnosed.
Understanding ovarian cysts
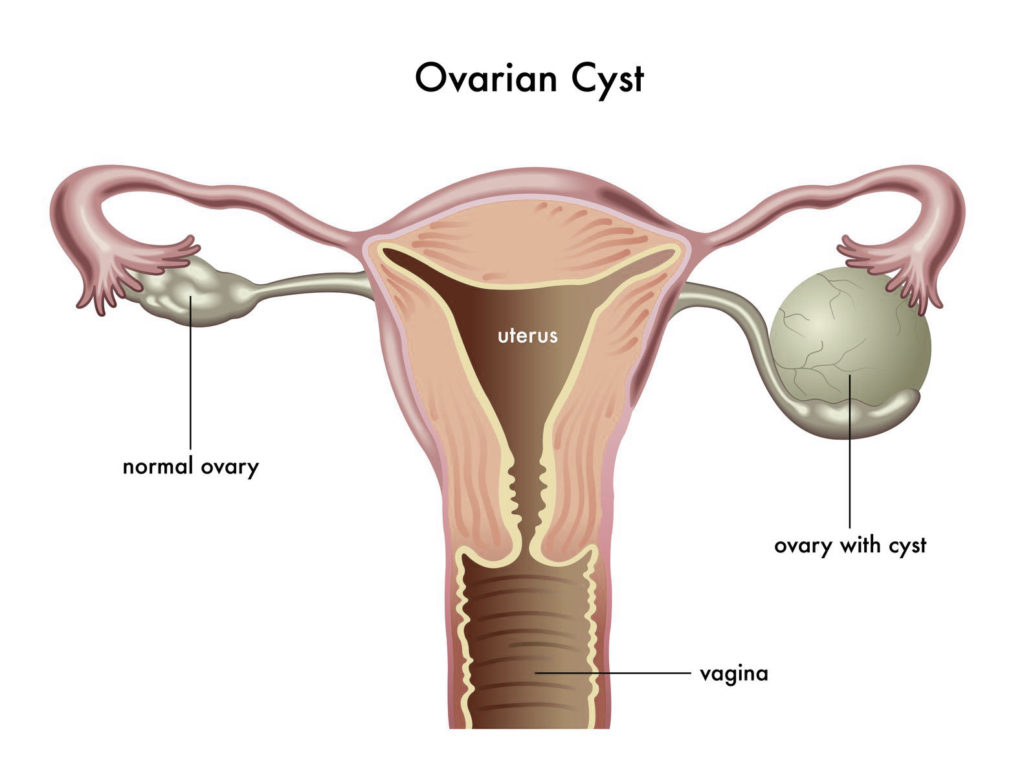
Ovarian cysts are small fluid filled sacs found on the ovaries. They are of various types like endometrioma cysts, functional cysts and dermoid cysts. Of these, the functional cysts are the most common type of cysts found in women.
Functional cysts are again divided into two types- the follicle cysts and corpus luteum cysts. A follicle is a sac like structure inside the ovary, in which an egg grows to maturity. During a woman’s menstrual cycle, this follicle breaks open to release the egg. However, in some cases, the follicle fails to break open, which leads the sac to fill with fluid, leading to the formation of an ovarian cyst.
Normally, the follicle dissolves away after releasing the egg. But in some women, this sac remains on the ovary, gets filled with the liquid and seal the opening over time, leading to the formation of a corpus luteum cyst.
Unlike the fluid-filled water cysts, dermoid cysts contain fat or hair tissues, while cystadenomas are non-malignant growth on the outer surface of the ovaries. Endometriomas are cysts that are formed due to the growth of endometrial tissue on the ovaries, which is classified as a separate condition called endometriosis.
Another cystic formation in the ovaries is polycystic ovary syndrome, where a woman’s ovaries develop a large number of smaller cysts, leading to enlarged ovaries. Leaving this condition untreated can lead to potential infertility in the long run.
Most often, ovarian cysts do not cause any symptoms. However, when the cyst grows bigger, it can lead to symptoms like abdominal bloating, pelvic pain during menstruation, painful intercourse, painful bowel movements, nausea and vomiting. If you suffer from any of these symptoms repeatedly, you might need immediate medical attention from our gynecologists.
Similarly, if the cysts are too big, it can lead to ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary) or the rupturing of the water cysts. This will cause severe pelvic pain, fever, faintness and dizziness. If not treated on time, this condition can lead to ovarian necrosis, which causes the ovarian tissues to die due to lack of blood.
Diagnosis and treatment of an ovarian cyst
To diagnose the presence of an ovarian cyst, our gynecologist will subject the patient to an ultrasound test and routine pelvic examination. The ultrasound imaging will help the specialist to determine the location, size, shape and composition of the cyst.
As most cysts disappear on their own after a few weeks or months, our gynecologist might not recommend a treatment plan on the first go. If it is present even after several scanning and is slowly increasing in size, then the patient will be prescribed a treatment plan.
Our gynecologists usually treat ovarian cysts with the help of oral contraceptives, which prevent ovulation and development of new cysts. These contraceptive pills also reduce the chance of ovarian cancer in women. Sometimes, water cysts have to be surgically removed through a laparoscopy or keyhole surgery. The keyhole surgery is performed by making a tiny incision near the patient’s navel and inserting the surgical instrument to remove the cyst.
Women must remain cautious about their reproductive health at all times. If you suffer from any of the symptoms discussed above, consult with our gynecologists at the earliest. Early detection and cure will ensure better health and quality of life.
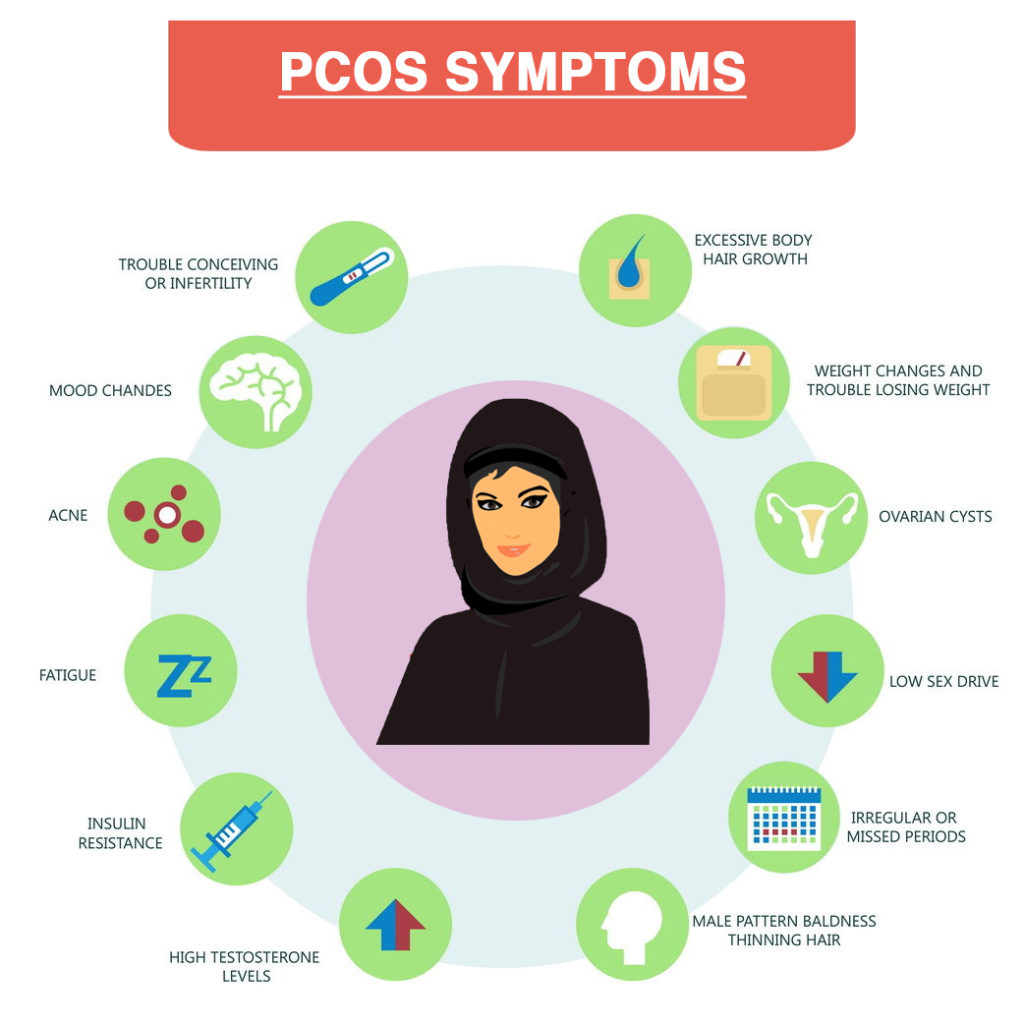
 These cysts are actually immature follicles. In normal menstrual cycle, follicle develops and grows to form an egg which ovulates, but in PCOS follicular development is arrested at early stage due to disturbed ovarian function and they form multiple cysts
These cysts are actually immature follicles. In normal menstrual cycle, follicle develops and grows to form an egg which ovulates, but in PCOS follicular development is arrested at early stage due to disturbed ovarian function and they form multiple cysts